
Location targeting is one of the most overlooked settings in Google Ads. You can target the whole world, but why would you? Usually, people select their target country or a few, which is OK. Advertisers look at location as a part of the target audience. Hence, most of them specify a country and never look back.
And that could be a mistake…
Locations in Google Ads can do more than that. It can be used to optimize your campaigns, reduce spend and CPA, and increase your ROI (return on investment).
Let’s take a look at how we can use location targeting to our advantage.
How Google Ads Location Targeting Works
Contrary to what many think, Google uses a set of various signals to determine users’ location.
For instance, a user’s IP address offers a general indication of their geographic region. But there might be instances where IP address is tied to a provider’s location and not the user’s location. This is why some people might see ads tailored to Los Angeles, although they might be in San Francisco.
Device settings may provide the option for users to share more precise location data, and for those on mobile devices, GPS data can pinpoint a location with remarkable accuracy. With so many people on mobile phones, users’ locations have indeed become more accurate.
Then, there is your browser that can also provide a location and your online behavior. Don’t forget that whatever you do online is tracked by someone. Always. Scary? It shouldn’t be, as it’s anonymous data. Well, most of it.
And don’t forget that it’s never 100% accurate.
Types of location targeting available
Google Ads provides several ways to target the location of your audience.
First, is when you select a country. It will also recommend a country based on your account details. But you can just enter any location you want.

But you can get more detailed and select cities or regions, even zip codes.

The second is when you target a radius. This is more advanced, but sometimes it works great.

This is Google’s office in San Francisco with a 1-mile radius target. I can write ads like “Hey, do you work at Google? Then we have a special discount for you”. Other people will see it, too, of course since they are in that radius. But most likely, they won’t click on the ad.
And then, there is a setting that allows you to adjust how “precise” the targeting is. Well, it’s not exactly that, but I will explain.

The first option, which is recommended by Google, will include people not only from a specific location but also people who express interest in that location. For example, people who google “hotels in San Francisco”, but not being in San Francisco. You see how this could help your business. But on the other hand, you might be spending additional dollars if Google somehow makes a mistake in interpreting users’ data.
In this case, you’re better off selecting the second option. This limits targeting to an actual physical location. Later, once your campaigns are converting, you can change this setting to include broader traffic.
Don’t forget that locations are added to the campaign level. You can’t add them to ad groups. This means that if you want to target two different countries, you can either add both of them to one campaign or create two campaigns for those two locations.
Optimizing campaigns with locations
Now that we know how locations work and what types there are, let’s see how we can use that information to optimize our campaigns.
It’s important to understand that it’s not always work. Sometimes, just adding your target country is fine. For example, in smaller countries, targeting options are limited. The USA has zip code targeting, and it works great, but Poland doesn’t have it. In Germany, zip code targeting has a limited reach and won’t work either.
Never use any features just for the sake of using them. Make sure you have a need (limit your audience, reduce cost, etc.), or you have tested it and you see that it works.
Always use one location per campaign
Don’t put several locations under the same campaign, as it is harder to optimize. Imagine you have 10 ad groups under one campaign, and that campaign targets 3 countries. It is hard to understand in which countries your keywords are performing better. Sure, there are some reports that help you drill down, but your options for controlling costs or bids for specific locations are limited.
There are always exclusions to the rule. For example, with niche keywords, you don’t want several campaigns for just a few keywords or keywords with low search volume unless the countries speak different languages.
You also want to have it under one campaign if you’re using automated bidding strategies as the algorithm will learn faster with more conversions under one campaign. For example, all English-speaking countries.
When you add several countries, you have control over the bid adjustment for each location, but that’s it. You can either increase or decrease bids. But that means you can’t control each individual keyword. So you lose a bit of control.
So, if I take a country and input a percentage by which I want the bids to be increased, Google will just take all the keywords and increase the bids if the user is from that country.

The downside of this is when you go to your individual keywords and change the bids there, you have to remember that the adjusted bid is on the country level. See, it’s a bit confusing. And the more countries you have in one campaign, the more complicated it becomes.
Breaking down one country
Now, let’s take it to the next level. You can break down each country further. This gives you even more control.
Take the US for example. Break it down by state. This way, you will be able to adjust bids at the state level to maximize conversions.
Take a look here.

We have several states, and I already see that some conversions are more expensive than others. I can easily reduce the bids for those states and increase them for the other states to try and get more clicks.
This works great when you have a limited budget, but you’re in a big country such as the US, Australia, and the UK. There is a big chance that not all people in your country will want what you offer due to many reasons. On top of that, there are differences in competition and cost in different parts of the country. For example, in the US, California and New York have higher costs per click.
Even if you’re on CPA bidding, seeing data breakdown by state gives you additional insights. You can exclude expensive states, and focus on the ones with lower CPA.
And you can go even further. Use cities to break down states. If you have enough traffic, you will notice that some cities might not convert as well. With detailed control, you can save your budget and direct it to better-converting locations.
ZIP codes for local businesses
You can even drill down to zip codes. Again, not in all countries. But I had very good results in the US. This is also great if your business serves in a particular location, like a flower shop or auto repair shop.
Having this detailed location targeting gives you the ability to exclude locations that would either never convert, or you would not be able to serve them.
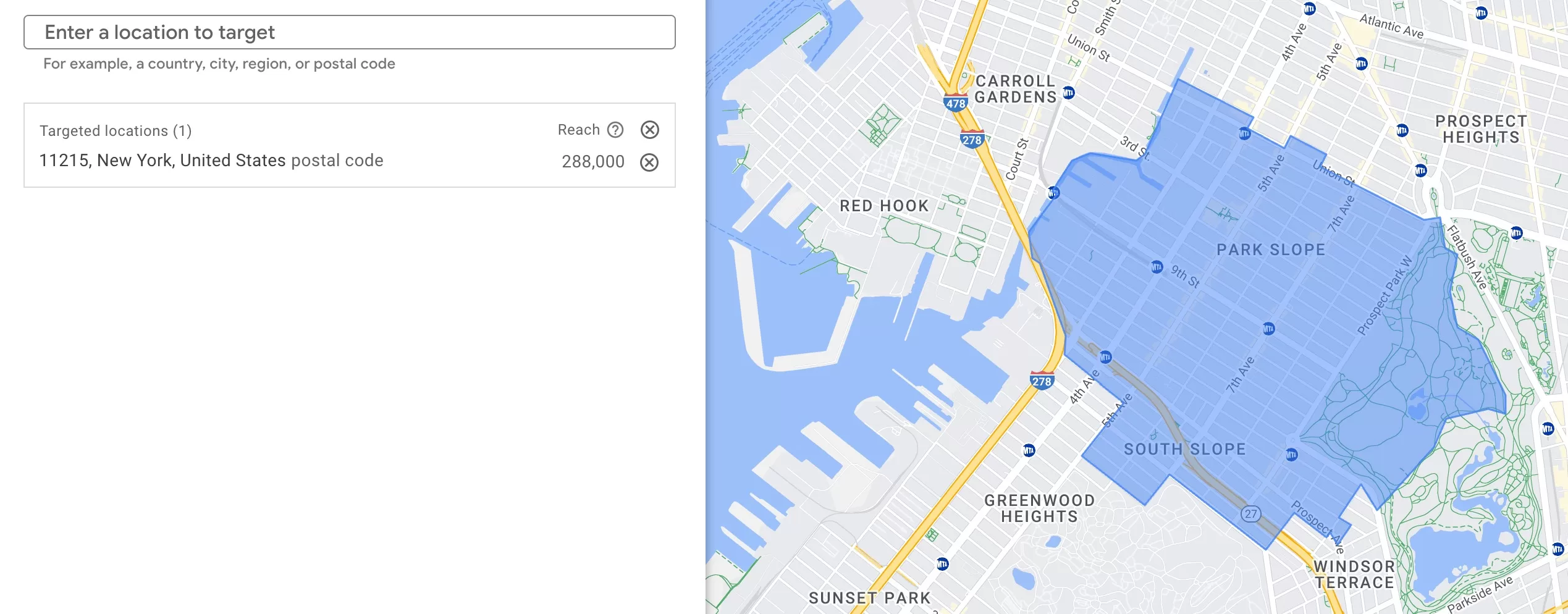
I can add only one zip code where my business is located and write localized ads, such as “Great coffee only 5 mins away” or “Flower shop around the corner.”
Or I can add several zip codes around my area and see if people are coming from those locations.

New York is a big city, and if I have a local business, there is no way someone will go from one end to another to buy from me. I better concentrate on the area around me.
Excluding locations also helps.
This is a “reverse” optimization (patent pending). Instead of adding locations you want to use, just exclude the ones that don’t perform. What’s the difference, you ask? Well, because Google is not 100% accurate in determining location.
Also, exclusions take priority over inclusions. In case you’re getting traffic from places you are not targeting, you should just exclude everything except your target location.
You can target the whole country and exclude some states or cities. For example, competition is higher in capital cities. So why not just exclude it, get your campaign performing and sales coming it, and then include the rest?
You might also want to optimize locations just based on shipping cost or time. For example, you might start with all the states except Alaska. Now, there is nothing wrong with that state in general, but, you know, you might think that the shipping will take too long. Or that the audience in Alaska has no use for your product.
Either way, you continue excluding locations until only performing ones are left. As you might have guessed, this takes longer and requires more spending. Because, in a sense, you start broad and narrow down instead of starting narrow and then widening your locations.
Combining locations and keywords
Although this is also an optimization technique, I wanted it to be a separate one from the one mentioned above. Take a look at these searches:

This is only targeting New York City. You see that keywords with phrases “near me” have a lot higher search volume than just “pizza in new york”. It might be different for other keywords. However, this shows that keywords are an important layer of location targeting.
Let’s start with “coffee near me”. Obviously, you can’t target the whole USA. You have to pick a specific location, which is probably a walking distance from a user. Those phrases will be in a separate campaign.
But when we talk about “pizza in new york”, would you target just New York? What about the whole state or country? What if people are planning to visit New York from another part of the state, or even a different state? You will exclude these people, but they may be your clients.
Keywords tell a lot, and you should take that into consideration. Sometimes you put them in the same category and limit location targeting, other times it is more beneficial to broaden location targeting because the keyword it self limits it.
Whenever you’re ready, there are two ways I can help you:
- Book a FREE call with me. During a 30-minute call, we can go through your account and identify growth opportunities or do a quick audit to see what can be improved instantly. Short call, big gains.
- Subscribe to my FREE weekly newsletter. Don’t miss new articles. Get them straight into your inbox.
- Learn Google Search Ads in 4 weeks. Stop wasting money on campaigns that don’t work. Let me guide you step-by-step to your first success with Google Ads.
I share weekly tips on how to create, manage, and scale Google Ads campaigns. Subscribe to my free newsletter.
I’m also down with connecting on LinkedIn.
Or follow me on X, for some quick updates and fast insights.